Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
佐藤 達彦; 渡辺 立子; 加瀬 優紀*; 鶴岡 千鶴*; 鈴木 雅雄*; 古澤 佳也*; 仁井田 浩二*
no journal, ,
粒子線による細胞致死効果は、細胞の種類やイオン種に依存することが知られている。しかし、現在、粒子線治療における治療効果推定のために使われている生物学的線量は、その依存性を考慮していない。そこで、粒子輸送計算コードPHITSにマイクロドジメトリック運動学モデルを組合せ、細胞・イオン種依存性を考慮可能な新たな生物学的線量評価手法を構築した。そして、その手法を用いて、実際の粒子線治療場におけるさまざまな細胞に対する生物学的線量を計算した。その結果、腫瘍部位における生物学的線量の絶対値は、細胞の種類により最大8%変化するものの、その照射表面からの深さに対する相対値は、細胞の種類に依存しないことがわかった。
 with carbon-ion microbeam
with carbon-ion microbeam坂下 哲哉; 鈴木 芳代; 浜田 信行*; 深本 花菜*; 横田 裕一郎; 舟山 知夫; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
原子力機構高崎量子応用研究所のイオン照射研究施設(TIARA)には高LET炭素イオンビームをマイクロビーム化し細胞等の生物試料に照射することが可能なマイクロビーム照射施設がある。私たちは、多細胞生物である線虫の神経組織に、この炭素イオンマイクロビームを照射し神経系の機能である学習行動に影響が及ぶかどうかを検討してきた。これまでに、神経麻酔を施した線虫へのマイクロビーム照射実験から、神経機能を停止させた場合には、学習行動への影響が観られないことを確認した。また、ブロードビーム照射実験からは、学習過程の途中に炭素イオンを被ばくすると学習行動の変化が生じることを明らかにしている。そのため、学習過程の途中の生理的な状態が、放射線が線虫の学習行動を変化させるときに重要な鍵となることが示唆された。現在、 TAS(Total Analysis Systems)を用いて、神経麻酔をしない状態の線虫に炭素イオンマイクロビームを照射する実験系の構築を進めている。将来このシステムを用いた炭素イオンマイクロビーム実験を行う予定である。
TAS(Total Analysis Systems)を用いて、神経麻酔をしない状態の線虫に炭素イオンマイクロビームを照射する実験系の構築を進めている。将来このシステムを用いた炭素イオンマイクロビーム実験を行う予定である。
横田 裕一郎; 舟山 知夫; 浜田 信行*; 坂下 哲哉; 鈴木 芳代; 武藤 泰子; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
放射線抵抗性で治療困難な腫瘍を克服するため、重粒子線と薬剤の併用効果についての知見を増やす必要がある。われわれは、ヒト子宮頚部癌細胞HeLa株における炭素線とテロメラーゼ阻害剤MST-312の併用効果について、コロニー形成法を用いて調べた。細胞は1 MのMST-312添加/無添加で24時間培養した後、炭素線(LET:110keV/
MのMST-312添加/無添加で24時間培養した後、炭素線(LET:110keV/ m)又は
m)又は 線を照射した。照射細胞の生存率は、MST-312添加により相加的に低下した。放射線とMST-312は、癌細胞の増殖能を独立したメカニズムで不活化するかもしれない。照射細胞の生存率を非照射細胞の10%に低下させる線量は、MST-312前処理により、炭素線では1.2Gyから0.5Gy、
線を照射した。照射細胞の生存率は、MST-312添加により相加的に低下した。放射線とMST-312は、癌細胞の増殖能を独立したメカニズムで不活化するかもしれない。照射細胞の生存率を非照射細胞の10%に低下させる線量は、MST-312前処理により、炭素線では1.2Gyから0.5Gy、 線では5.4Gyから4.0Gyに低下した。MST-312前処理は、重粒子線癌治療の根治線量を低減する可能性がある。
線では5.4Gyから4.0Gyに低下した。MST-312前処理は、重粒子線癌治療の根治線量を低減する可能性がある。
舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 横田 裕一郎; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
重イオンが細胞に及ぼす影響を明らかにするためには、細胞を正確に狙い、あらかじめ設定した個数のイオンを照射することができる、細胞照射用重イオンマイクロビーム装置が必要になる。そこで、私たちの研究グループでは、これまでコリメーション式重イオンマイクロビーム装置を用いた細胞照射応答の研究を進めてきた。しかし、コリメーション式重イオンマイクロビーム装置では、照準できるビームサイズに限界があった。そこで、原子力機構TIARAのAVFサイクロトロンの垂直ビームラインに、四重極磁気レンズで重イオンビームを最小径1 mまで微小化し、大気取り出しをすることができる新たなマイクロビーム装置を設置した。この装置を用いて、細胞への照準照射を実現するために、ビームライン直下に細胞照準用倒立顕微鏡と、細胞試料用電動ステージを設置した。このシステムを用いてHeLa細胞への照準照射実験を行い、細胞にヒットしたイオンの位置を確認したところ、細胞は3
mまで微小化し、大気取り出しをすることができる新たなマイクロビーム装置を設置した。この装置を用いて、細胞への照準照射を実現するために、ビームライン直下に細胞照準用倒立顕微鏡と、細胞試料用電動ステージを設置した。このシステムを用いてHeLa細胞への照準照射実験を行い、細胞にヒットしたイオンの位置を確認したところ、細胞は3 m以下に集束したビームで正確に照射されていた。これらの結果は、集束式重イオンマイクロビームによる細胞への照準照射技術が確立できたことを意味する。
m以下に集束したビームで正確に照射されていた。これらの結果は、集束式重イオンマイクロビームによる細胞への照準照射技術が確立できたことを意味する。
Bolton, P.; 阿部 光幸*; 赤城 卓*; Nuesslin, F.*; 堀 利彦; 岩下 芳久*; 河西 俊一; 近藤 公伯; 前田 拓也; Molls, M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The rapid advancement of high power laser technology combined with laser-accelerated ion yields from intense laser-plasma interactions sustains a strong interest in the development of integrated laser-driven ion accelerator systems (ILDIAS) that can be used for laser-driven ion beam radiotherapy (L-IBRT). A prime motivation is the promise of significantly reduced size and cost that would afford much greater patient access. Bunch duration of several nanoseconds and high peak current (with a low duty factor) make laser-driven ion irradiation unique. En route to a compact laser-driven "clinical" radiotherapeutic facility it is essential to develop multipurpose "preclinical" or test beamlines that can be used for (1) testing suitable transport optics, diagnostics and control instrumentation, (2) medical and radiobiological studies at the cellular level and in tissue to validate the radiobiological effectiveness of laser-driven ion beam radiotherapy and (3) applications to nonmedical science and technology. Preclinical and clinical beamline development calls for delivering proton energies near 50 MeV and at least 80 MeV respectively with beam energy spread and dose accuracy at one to few percent levels. Control instrumentation and diagnostics capable of single bunch resolution at required repetition rates will be essential to verify and optimize ILDIAS machine performance and capability. In the context of L-IBRT we will discuss the ILDIAS concept as well as beam delivery and instrumentation requirements.
山口 充孝; 神谷 富裕; 河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 藤巻 秀; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 伸*; 石川 真之介*; 小高 裕和*; 国分 紀秀*; et al.
no journal, ,
医学イメージング用途のSi/CdTeコンプトンカメラのプロトタイプの開発を行ってきた。コンプトンカメラヘッドが単一である場合、深度方向の空間分解能は低く3次元的に解像度の良い撮像は不可能である。分解能の改善のため、われわれは複数ヘッド型コンプトンカメラを提案してきた。今回、コンプトンカメラを用いた実験データとモンテカルロシミュレーション結果とを比較し、単一ヘッド装置の空間分解能を検証した。さらに、マルチヘッド化の影響調査のため、ダブルヘッド装置のシミュレーションによる分解能評価を行った。カメラヘッドは2枚のSiストリップ検出器と2枚のCdTeストリップ検出器からなる。モンテカルロシミュレーションにはGEANT4を用いたカメラシミュレーターを用いた。イメージングには、LM-ML-EM法を用いた。測定結果はシミュレーションによる結果とよく一致した。深度方向の空間分解能は、単一ヘッドの場合、おおよそ15mmであるが、ダブルヘッドの場合6mm程度に改善されることがシミュレーションにより示唆された。これらの結果はマルチヘッド化による3次元空間分解能の改善を示唆するものである。
余語 覚文
no journal, ,
Laser-acceleration of ions has been suggested as an alternative approach to conventional accelerators for ion beam radiotherapy (IBRT). To investigate the effects of high dose rate that is attributed to high ion current, short bunch irradiation we have developed an experimental setup that uses laser-accelerated protons. In-vitro human lung cancer cells: A549 pulmonary adenocarcinoma are irradiated with a laser-accelerated proton bunches of duration, 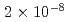 s and flux,
s and flux, 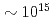 cm
cm s
s , amounting to single bunch absorbed dose at the 1 Gy level. The double-strand break (DSB) yield in cell DNA is analyzed using the phosphorylated histone H2AX (
, amounting to single bunch absorbed dose at the 1 Gy level. The double-strand break (DSB) yield in cell DNA is analyzed using the phosphorylated histone H2AX ( -H2AX) immunostaining method. By counting the number of
-H2AX) immunostaining method. By counting the number of  -H2AX foci apparent on the microscopic images, we estimate the DSB yield to be 41 DSBs/nucleus/Gy for single bunch irradiation of laser-accelerated protons. We determine the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) for DSB induction to be 1.47
-H2AX foci apparent on the microscopic images, we estimate the DSB yield to be 41 DSBs/nucleus/Gy for single bunch irradiation of laser-accelerated protons. We determine the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) for DSB induction to be 1.47 0.38 for a laser-accelerated proton beam at an average LET of 41 keV/
0.38 for a laser-accelerated proton beam at an average LET of 41 keV/ m. This RBE value is comparable to those for light ions delivered by conventional accelerators. Irradiation by laser-accelerated protons has been shown to be effective for DSB induction in cancer cell DNA. However, we observe no DNA DSB effects that can be attributed to the high-current irradiation when the beam flux is increased up to
m. This RBE value is comparable to those for light ions delivered by conventional accelerators. Irradiation by laser-accelerated protons has been shown to be effective for DSB induction in cancer cell DNA. However, we observe no DNA DSB effects that can be attributed to the high-current irradiation when the beam flux is increased up to 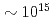 cm
cm s
s used in the present experiment.
used in the present experiment.
 -ray irradiation on locomotory behavior and mechanosensation in
-ray irradiation on locomotory behavior and mechanosensation in 
鈴木 芳代; 坂下 哲哉; 菊地 正博; 舟山 知夫; 横田 裕一郎; 服部 佑哉; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
We examined effects of  -ray and irradiation on the basal slowing response regarding to mechanosensation in
-ray and irradiation on the basal slowing response regarding to mechanosensation in 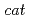 -
-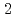 mutants that are deficient in a tyrosine hydroxylase for the synthesis of dopamine, and found that the
mutants that are deficient in a tyrosine hydroxylase for the synthesis of dopamine, and found that the  -induced reduction of the locomotory rate (motility) was not mediated by
-induced reduction of the locomotory rate (motility) was not mediated by 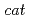 -
-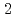 . Additionally, the results suggest that bacterial mechanosensation in
. Additionally, the results suggest that bacterial mechanosensation in 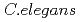 might be the dominant mechanism regulating locomotory rate, masking the effects of other stimuli such as IR. Furthermore, dose response pattern in locomotory rate of carbon ion-irradiated animals was similar to that of
might be the dominant mechanism regulating locomotory rate, masking the effects of other stimuli such as IR. Furthermore, dose response pattern in locomotory rate of carbon ion-irradiated animals was similar to that of  -irradiated animals, it can state that the effects of IR do not depend on LET within the dose we examined. Moreover we showed possibility that H
-irradiated animals, it can state that the effects of IR do not depend on LET within the dose we examined. Moreover we showed possibility that H O
O produced by IR might concern to the IR-induced reduction of locomotory rate.
produced by IR might concern to the IR-induced reduction of locomotory rate.